str = '我是一名学生' print(str[0]) #输出“我” print(str[-6]) #输出“我”

字符串切片:把数据对象的一部分拿出来
str = '我是一名学生' print(str[2:4]) #输出“一名” print(str[-4:-2]) #输出“一名”

#获取字符串长度:len() str = '我是一名学生' length = len(str) print(length)

函数
def interview(): #def是关键字 表示定义一个函数 print("把求职者带到3号会议室") print("请求职者 完成答卷") print("让测试经理来面试 求职者") print("让技术总监面试 求职者")
-
函数参数:
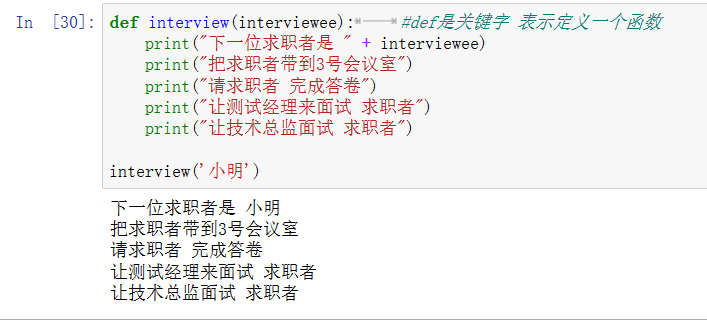
def interview(interviewee): #def是关键字 表示定义一个函数 print("下一位求职者是" + interviewee) print("把求职者带到3号会议室") print("请求职者 完成答卷") print("让测试经理来面试 求职者") print("让技术总监面试 求职者") interview('小明')
注:python中TAB和空格不能混用,否则会出错
列表:列表的内容可以改变
-
定义:
nameList = [] #空列表 a = [1, 2, 3.14, 'hello', [7,8,9] ] #非空列表
元组:元组的内容不可以改变
-
定义:
nameList = () #空元组 a = (1, 2, 3.14, 'hello') #非空元组
如果元组中只有一个元素,必须要在后面加上逗号。(a = (1, ))
定义元组还可以去掉圆括号,a = 1, 2, 3.14, 'hello'
-
判断元素是否在元组:
list1 = [1,2,3,4, 'hello'] tuple1 = (1,2,3,4, 'hello') ? if 'hello' in list1: print('hello 在列表中存在') ? if 'boy' not in tuple1: print('boy 在元组中不存在')
判断语句
def registerUser(): phone = input('请输入你的手机号码(不超过11个字符):') if len(phone) > 11: print('输入错误!手机号码超过了11个字符') # 还需要进一步判断 输入的是否全数字 elif not phone.isdigit() : print('输入错误!手机号码必须全是数字') # 判断是否以数字1 开头 elif not phone.startswith('1') : # startswith 是字符串对象的方法 print('输入错误!手机号码必须以数字1开头') else: print('手机号码输入正确') print('函数结束')
isdigit() 方法检测字符串是否只由数字组成,只对 0 和 正数有效。
startsWith() 方法用于检测字符串是否以指定的子字符串开始。
输入
def temperature(): tem = int(input("请输入今天的气温:")) ap = int(input("请输入今天的气压:")) if tem > 30 or tem < -8 or ap > 300 or tem < 20: print("不舒适") elif tem >25 and tem <= 30 and ap > 200 and ap <= 300: print("比较舒适") else: print("无法判断") temperature()
对象的方法
# var1 是一个列表对象 var1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] # 列表对象都有 reverse方法,该方法将列表元素倒过来 var1.reverse() print(var1)

字符串的方法
-
count:
# 调用字符串的count 方法,count 方法可以返回字符串对象包含了多少个参数指定的字符串 # 表示该字符串包含了两个 '我们' '我们今天不去上学,我们去踢足球'.count('我们')
-
find:在字符串中查找参数子字符串,并返回该参数字符串在其中第一个出现的位置索引
str1 = '我们今天不去上学,我们去踢足球' # 返回 0 , str1字符串中有两个 '我们' # find返回的是第一个 '我们' 的索引 0 pos1 = str1.find('我们')
-
split、splitlines:split经常用来从字符串中截取出我们想要的信息。
#用 | 作为源字符串str1的分割符 str1 = '小张:79 | 小李:88 | 小赵:83' pos1 = str1.split('|') print(pos1)

#splitlines把字符串按换行符进行切割 salary = ''' 小王 10000元 小李 20000元 小徐 15000元 ''' ? print(salary.splitlines())

-
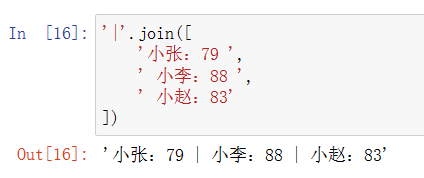
join:将列表中的字符串元素以某字符串为连接符,连接为一个字符串
'|'.join([ '小张:79 ', ' 小李:88 ', ' 小赵:83' ])
-
strip 、 lstrip 、 rstrip:
' 小 李:88 '.strip() #strip方法可以将 字符串前面和后面的空格删除,但是不会删除字符串中间的空格 ' 小 李:88 '.lstrip() #将字符串前面(左边)的空格删除,但是不会删除字符串中间和右边的空格 ' 小 李:88 '.rstrip() #将字符串后面(右边)的空格删除,但是不会删除字符串中间和左边的空格
-
replace:替换字符串里面所有指定的子字符串为另一个字符串
str1 = '我们今天不去上学,我们去踢足球' str1 = str1.replace('我们', '他们')
-
startswith 和 endswith
#startswith方法检查字符串是否以参数指定的字符串开头 #endswith方法检查字符串是否以指定的字符串结尾 str1 = '我们今天不去上学,我们去踢足球' str1.startswith('我们') # 返回 True str1.endswith('我们') # 返回 False def telephone(): tele = input("请输入手机号码:") if not tele.isdigit() or len(tele) != 11 or not tele.startswith('1'): print("手机号码输入格式错误") else: print("您的手机号码为:"+tele) telephone()
列表的方法
-
append:在列表后面添加一个元素
a = [1, 2, 3.14, 'hello'] ? # append 之后,a就变成了 [1, 2, 3.14, 'hello', '你好'] a.append('你好') print(a) ?