ead(target=woman, args=(m_tot, m_pop))
m.start()
w.start()
#结果
#男在上厕所
#女的拿到纸资源了
#>>>>>>解决死锁
#>>>>递归锁 : 只有一把钥匙,但是可以开所有锁,层层开锁
from multiprocessing import Process
from threading import Thread ,RLock import time,os def man(m_tot,m_pap): m_tot.acquire()#男的手中有一把钥匙获得厕所资源,把厕所锁上了 print('男在上厕所') time.sleep(1) m_pap.acquire()#男的拿纸资源 print('男的拿到纸资源了') time.sleep(1) print('男的上完厕所了') m_tot.release()#男的还纸资源 m_pap.release()#男的还厕所资源 def woman(m_tot,m_pap): m_pap.acquire() # 女的拿到一把钥匙,获得纸资源 print('女的拿到纸资源了') time.sleep(1) m_tot.acquire() # 女的拿厕所资源,把厕所锁上了 print('女在上厕所') time.sleep(1) print('女的上完厕所了') m_tot.release() # 女的还厕所资源 m_pap.release() # 女的还纸资源 if __name__ == '__main__': m_tot = RLock() m_pop = RLock() m = Thread(target=man,args=(m_tot,m_pop)) w = Thread(target=woman, args=(m_tot, m_pop)) m.start() w.start()
线程间的通信与进程的用法一样(线程可以不写__main__)
信号量
from threading import Semaphore

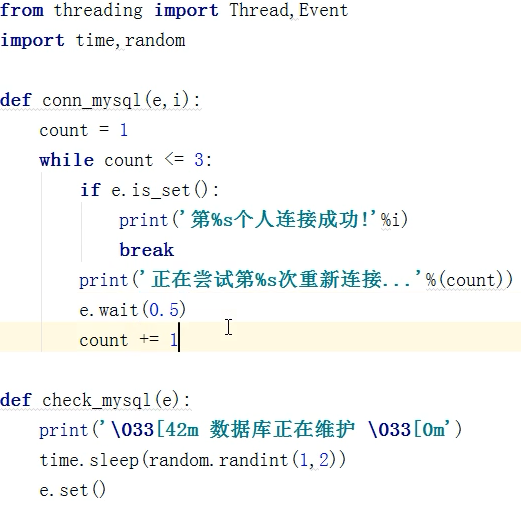
事件
from threading import Event
条件
from threading import Condition
条件是让程序员自行去调度线程的一个机制
# Condition涉及4个方法
# acquire()
# release()
# wait() 是指让线程阻塞住
# notify(int) 是指给wait发一个信号,让wait变成不阻塞
# int是指,你要给多少给wait发信号

定时器
from threading import Timer
Timer(time , func )
time :睡眠时间,(秒为单位)
func : 睡眠过后,要执行的函数
from threading import Timer
def func():
print('定时器')
Timer(3,func).start()