tup single plot function
plot_prediction <- function(data,
id,
alpha = 1,
size = 2,
base_size = 14) {
rmse_val <- calc_rmse(data)
g <- data %>%
ggplot(aes(index, value, color = key)) +
geom_point(alpha = alpha, size = size) +
theme_tq(base_size = base_size) +
scale_color_tq() +
theme(legend.position = "none") +
labs(
title = glue(
"{id}, RMSE: {round(rmse_val, digits = 1)}"),
x = "", y = "")
return(g)
}
我们设置 id = split_id,在 Slice11 上测试函数。
ret %>%
plot_prediction(id = split_id, alpha = 0.65) +
theme(legend.position = "bottom")
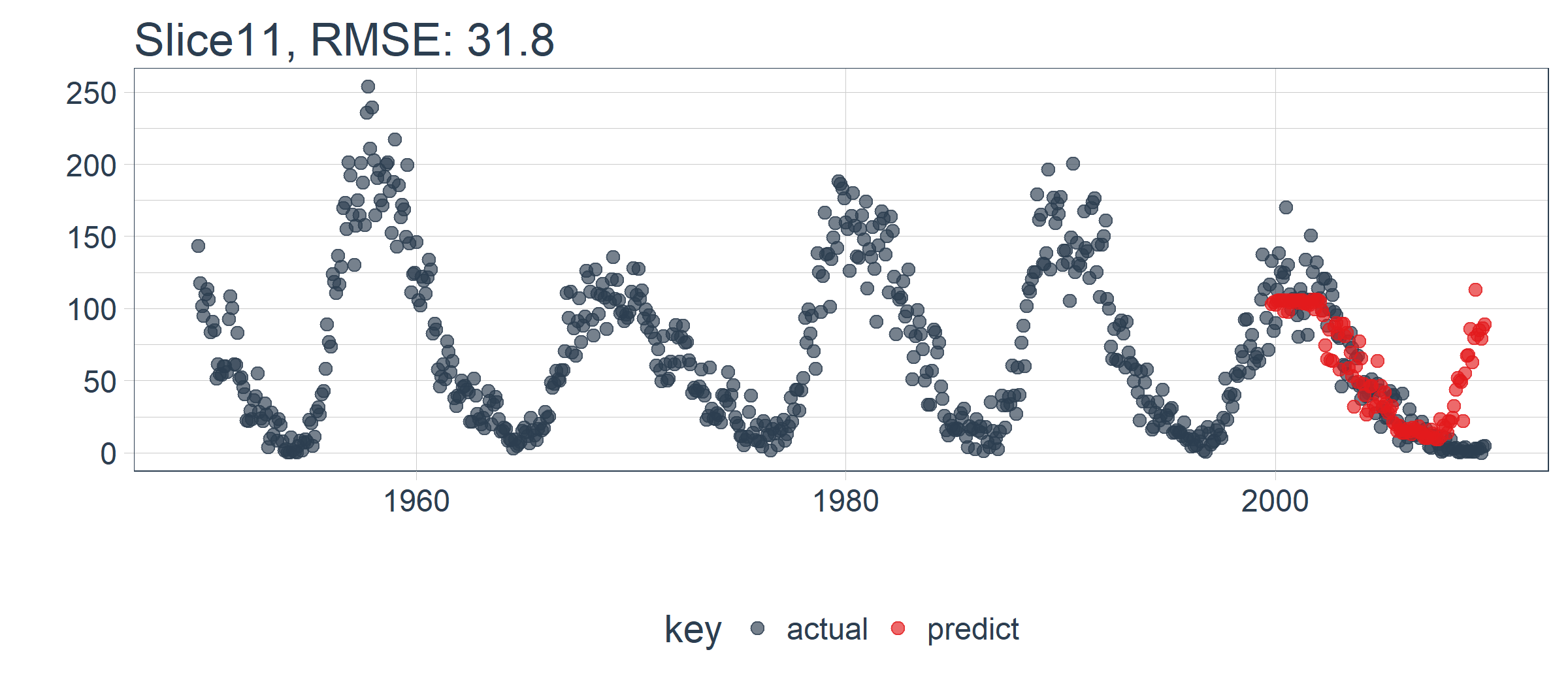
LSTM 模型表现相对较好! 我们选择的设置似乎产生了一个不错的模型,可以捕捉到数据中的趋势。预测在下一个上升趋势前抢跑了,但总体上好过了我的预期。现在,我们需要通过回测来查看随着时间推移的真实表现!
5.2 在 11 个样本上回测 LSTM 模型
一旦我们有了能在一个样本上工作的 LSTM 模型,扩展到全部 11 个样本上就相对简单。我们只需创建一个预测函数,再套用到 rolling_origin_resamples 中抽样计划包含的数据上。
5.2.1 构建一个 LSTM 预测函数
这一步看起来很吓人,但实际上很简单。我们将 5.1 节的代码复制到一个函数中。我们将它作为一个安全函数,对于任何长时间运行的函数来说,这是一个很好的做法,可以防止单个故障停止整个过程。
predict_keras_lstm <- function(split,
epochs = 300,
...) {
lstm_prediction <- function(split,
epochs,
...) {
# 5.1.2 Data Setup
df_trn <- training(split)
df_tst <- testing(split)
df <- bind_rows(
df_trn %>% add_column(key = "training"),
df_tst %>% add_column(key = "testing")) %>%
as_tbl_time(index = index)
# 5.1.3 Preprocessing
rec_obj <- recipe(value ~ ., df) %>%
step_sqrt(value) %>%
step_center(value) %>%
step_scale(value) %>%
prep()
df_processed_tbl <- bake(rec_obj, df)
center_history <- rec_obj$steps[[2]]$means["value"]
scale_history <- rec_obj$steps[[3]]$sds["value"]
# 5.1.4 LSTM Plan
lag_setting <- 120 # = nrow(df_tst)
batch_size <- 40
train_length <- 440
tsteps <- 1
epochs <- epochs
# 5.1.5 Train/Test Setup
lag_train_tbl <- df_processed_tbl %>%
mutate(
value_lag = lag(value, n = lag_setting)) %>%
filter(!is.na(value_lag)) %>%
filter(key == "training") %>%
tail(train_length)
x_train_vec <- lag_train_tbl$value_lag
x_train_arr <- array(
data = x_train_vec, dim = c(length(x_train_vec), 1, 1))
y_train_vec <- lag_train_tbl$value
y_train_arr <- array(
data = y_train_vec, dim = c(length(y_train_vec), 1))
lag_test_tbl <- df_processed_tbl %>%
mutate(
value_lag = lag(value, n = lag_setting)) %>%
filter(!is.na(value_lag)) %>%
filter(key == "testing")
x_test_vec <- lag_test_tbl$value_lag
x_test_arr <- array(
data = x_test_vec, dim = c(length(x_test_vec), 1, 1))
y_test_vec <- lag_test_tbl$value
y_test_arr <- array(
data = y_test_vec, dim = c(length(y_test_vec), 1))
# 5.1.6 LSTM Model
model <- keras_model_sequential()
model %>%
layer_lstm(
units = 50,
input_shape = c(tsteps, 1),
batch_size = batch_size,
return_sequences = TRUE,
stateful = TRUE) %>%
layer_lstm(
units = 50,
return_sequences = FALSE,
stateful = TRUE) %>%
layer_dense(units = 1)
model %>%
compile(loss = 'mae', optimizer = 'adam')
# 5.1.7 Fitting LSTM
for (i in 1:epochs) {
model %>%
fit(x = x_train_arr,
y = y_train_arr,
batch_size = batch_size,
epochs = 1,
verbose = 1,
shuffle = FALSE)
model %>% reset_states()
cat("Epoch: ", i)
}
# 5.1.8 Predict and Return Tidy Data
# Make Predictions
pred_out <- model %>%
predict(x_tes