一、简介
消息处理机制主要涉及到这几个类:
1.Looper
2.MessageQueue
3.Message
4.Handler
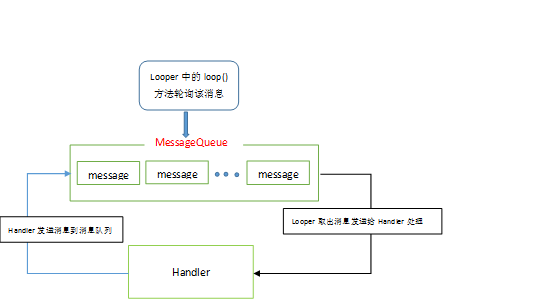
二、源码分析
Looper.class的关键源码:
//保存Looper对象,在android中每创建一个消息队列,就有一个并且是唯一一个与之对应的Looper对象 static final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>(); //主线程的Looper private static Looper sMainLooper; //消息队列 final MessageQueue mQueue; final Thread mThread; //子线程中通过调用该方法来创建消息队列 public static void prepare() { prepare(true); } private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) { if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) { throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread"); } sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed)); } //主线程调用该方法来创建消息队列 public static void prepareMainLooper() { prepare(false); synchronized (Looper.class) { if (sMainLooper != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared."); } sMainLooper = myLooper(); } } //实例化Looper,创建消息队列,获取当前线程 private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) { mQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed); mThread = Thread.currentThread(); } //调用loop方法开启消息循环 public static void loop() { //获取当前的Looper对象,若为null,抛出异常 final Looper me = myLooper(); if (me == null) { throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread."); } //获取当前的消息队列,进入循环 final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue; for (;;) { //调用next()方法从消息队列中获取消息,如果为null,结束循环;否则,继续执行(有可能会阻塞) Message msg = queue.next(); if (msg == null) { return; } ...... try { //调用handler的dispatchMessage(msg)分发消息 msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg); } finally { ...... } //回收消息资源 msg.recycleUnchecked(); } } //消息循环退出 public void quit() { mQueue.quit(false); } public void quitSafely() { mQueue.quit(true); }
消息循环退出过程
从上面可以看到loop()方法是一个死循环,只有当MessageQueue的next()方法返回null时才会结束循环。那么MessageQueue的next()方法何时为null呢?
在Looper类中我们看到了两个结束的方法quit()和quitSalely()。
两者的区别就是quit()方法直接结束循环,处理掉MessageQueue中所有的消息。
quitSafely()在处理完消息队列中的剩余的非延时消息(延时消息(延迟发送的消息)直接回收)时才退出。这两个方法都调用了MessageQueue的quit()方法
MessageQueue.class 的关键源码:
MessageQueue中最重要的就是两个方法:
1.enqueueMessage()向队列中插入消息
2.next() 从队列中取出消息
/* *MessageQueue中enqueueMessage方法的目的有两个: *1.插入消息到消息队列 *2.唤醒Looper中等待的线程(如果是即时消息并且线程是阻塞状态) */ boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) { //发送该消息的handler为null,抛出异常 if (msg.target == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Message must have a target."); } //此消息正在被使用 if (msg.isInUse()) { throw new IllegalStateException(msg + " This message is already in use."); } synchronized (this) { //此消息队列已经被放弃了 if (mQuitting) { IllegalStateException e = new IllegalStateException( msg.target + " sending message to a Handler on a dead thread"); msg.recycle(); return false; } msg.markInUse(); msg.when = when; //消息队列的第一个元素,MessageQueue中的成员变量mMessages指向的就是该链表的头部元素。 Message p = mMessages; boolean needWake; if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) { //如果此队列中头部元素是null(空的队列,一般是第一次),或者此消息不是延时的消息,则此消息需要被立即处理, //将该消息作为新的头部,并将此消息的next指向旧的头部。如果是阻塞状态则需要唤醒。 msg.next = p; mMessages = msg; needWake = mBlocked; } else { //如果此消息是延时的消息,则将其添加到队列中, //原理就是链表的添加新元素,按照时间顺序来插入的,这样就得到一条有序的延时消息链表