Redis是一个开源的使用ANSI C语言编写、支持网络、可基于内存亦可持久化的日志型、Key-Value数据库,并提供多种语言的API。
Redis支持存储的value类型包括字符串(String), 哈希(Hash), 列表(list), 集合(set) 和 有序集合(sorted set)。
Redis官方文档:https://redis.io
Redis服务端的安装可参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/gdjlc/p/9857064.html
Redis客户端可视工具可使用:Redis Desktop Manager
一、Python安装Redis模块
pip3 install redis
二、连接Redis数据库
1、直接连接
# Reids默认有db0至db15共16个数据库,db=0表示选择db0 # decode_responses=True表示将返回结果decode,即将bytes类型改为默认utf-8,这样才能显示中文 r = redis.Redis(host='localhost',password='123456',db=0,decode_responses=True)
上面连接字符串也可以写成这样
dbconfig = {'host':'localhost', 'password':'123456', 'db':0, 'decode_responses':True}
r = redis.Redis(**dbconfig)
2、连接池
使用connection pool来管理对一个redis server的所有连接,预先创建多个连接,当需要进行数据库访问时,无需重新新建数据库连接,而是从连接池中取出一个空闲的数据库连接,避免每次建立、释放连接的开销,提高性能。
pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='localhost',password='123456',db=0,decode_responses=True) r = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
三、Redis的使用
1、字符串(String)
一个name对应一个字符串值来存储。如下图所示

部分方法的源码说明:
# 设置单个值(不存在则创建,存在则修改),可以设置过期时间,可以设置name是否存在时才设置value def set(self, name, value, ex=None, px=None, nx=False, xx=False): """ Set the value at key ``name`` to ``value`` ``ex`` sets an expire flag on key ``name`` for ``ex`` seconds. ``px`` sets an expire flag on key ``name`` for ``px`` milliseconds. ``nx`` if set to True, set the value at key ``name`` to ``value`` only if it does not exist. ``xx`` if set to True, set the value at key ``name`` to ``value`` only if it already exists. """ # 批量设置值(同样不存在则创建,存在则修改) def mset(self, mapping): """ Sets key/values based on a mapping. Mapping is a dictionary of key/value pairs. Both keys and values should be strings or types that can be cast to a string via str(). """ # 获取值,key不存在返回None def get(self, name): """ Return the value at key ``name``, or None if the key doesn't exist """ # 批量获取值 def mget(self, keys, *args): """ Returns a list of values ordered identically to ``keys`` """
使用实例:
import redis r = redis.Redis(host='localhost',password='123456',db=0,decode_responses=True) # 设置单个值(不存在则创建,存在则修改) r.set('str_key1', '我是str_key1的值') # 获取值、值的字节长度(1个汉字占3个字节) print('str_key1值:{},字节长度:{}'.format(r.get('str_key1'), r.strlen('str_key1'))) # 输出:我是str_key1的值,字节长度:20 # 在值后面追加内容 r.append('str_key1', '[这里追加的内容]') print('str_key1值:{}'.format(r.get('str_key1'))) # 输出:我是str_key1的值[这里追加的内容] # 批量设置值(同样不存在则创建,存在则修改) r.mset({'str_key1':'value1','str_key2':'value2'}) # 批量获取 print('批量获取值:{}'.format(r.mget('str_key1','key2'))) # 输出:['value1', None]
2、 哈希(Hash)
一个name对应一个字典来存储。如下图所示
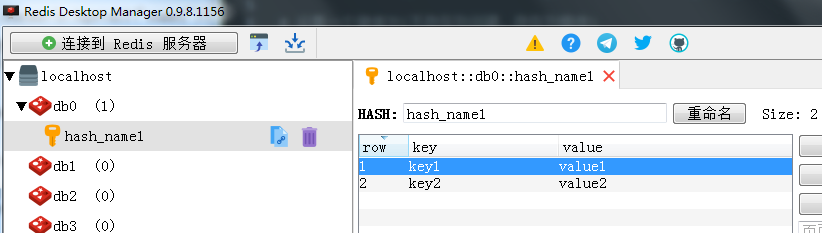
部分方法的源码说明:
# 设置一个键值对(不存在则创建,存在则修改),成功返回1否则返回0 def hset(self, name, key, value): """ Set ``key`` to ``value`` within hash ``name`` Returns 1 if HSET created a new field, otherwise 0 """ # 批量设置值 def hmset(self, name, mapping): """ Set key to value within hash ``name`` for each corresponding key and value from the ``mapping`` dict. """ # 返回一个键值对的值 def hget(self, name, key): "Return the value of ``key`` within the hash ``name``" # 返回所有键值对