|
onDestroy();
Log.d("MyIntentService", "onDestroy executed");
}
}
以上代码做了几件事:
1、提供了一个无参的构造方法,并且调用了父类的有参构造函数(这个就不需要我说为什么了吧);
2、子类实现父类的onHandleIntent()抽象方法,这个方法好就好在,它是一个已经运行在子线程中的方法。也就是说,服务调用了它,那么执行的逻辑就如同Thread子线程。
onHandleIntent = Thread().start() + stopSelf()
3、onHandleIntent()执行完后会销毁服务?会selfStop()?接着往下看代码。
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(2)在xml文件中,创建一个MyIntentService服务按钮:
<Button
android:id="@+id/start_intent_service"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/intent_service"/>
(3)接下来,修改MainActivity中的代码:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button startIntentService = (Button) super.findViewById(R.id.start_intent_service);
startIntentService.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Log.d("MyIntentService", "MainActivity Thread id is " + Thread.currentThread().getId()); // 查看主线程的id
Intent intentService = new Intent(getBaseContext(), MyIntentService.class); startService(intentService);
}
});
}
}
(4)最后,在AndroidMainfest中注册服务:
<service android:name=".MyIntentService" />
【结果】:直接看一下代码执行的效果。
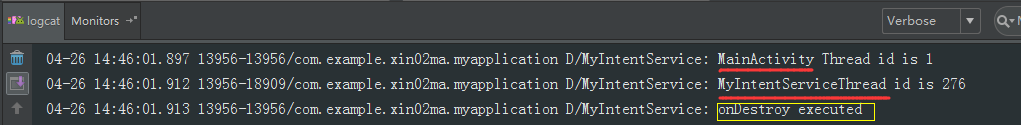
从打出的LOG可以看出:
(1)MyIntentService和MainActivity所在进程的id是不一样的;
(2)onHandleIntent()方法在执行完逻辑后确实销毁了服务,效果等同于stopSelf()。
从上面的分析可以看出onHandleIntent()方法确实相当的好用!
|