mse = sd(rmse))
## # Rolling origin forecast resampling
## # A tibble: 1 x 2
## mean_rmse sd_rmse
## <dbl> <dbl>
## 1 34.4 13.0
5.2.4 可视化回测的结果
我们可以创建一个 plot_predictions() 函数,把 11 个回测样本的预测结果绘制在一副图上!!!
plot_predictions <- function(sampling_tbl,
predictions_col,
ncol = 3,
alpha = 1,
size = 2,
base_size = 14,
title = "Backtested Predictions") {
predictions_col_expr <- enquo(predictions_col)
# Map plot_split() to sampling_tbl
sampling_tbl_with_plots <- sampling_tbl %>%
mutate(
gg_plots = map2(
!! predictions_col_expr, id,
.f = plot_prediction,
alpha = alpha,
size = size,
base_size = base_size))
# Make plots with cowplot
plot_list <- sampling_tbl_with_plots$gg_plots
p_temp <- plot_list[[1]] + theme(legend.position = "bottom")
legend <- get_legend(p_temp)
p_body <- plot_grid(plotlist = plot_list, ncol = ncol)
p_title <- ggdraw() +
draw_label(
title,
size = 18,
fontface = "bold",
colour = palette_light()[[1]])
g <- plot_grid(
p_title,
p_body,
legend,
ncol = 1,
rel_heights = c(0.05, 1, 0.05))
return(g)
}
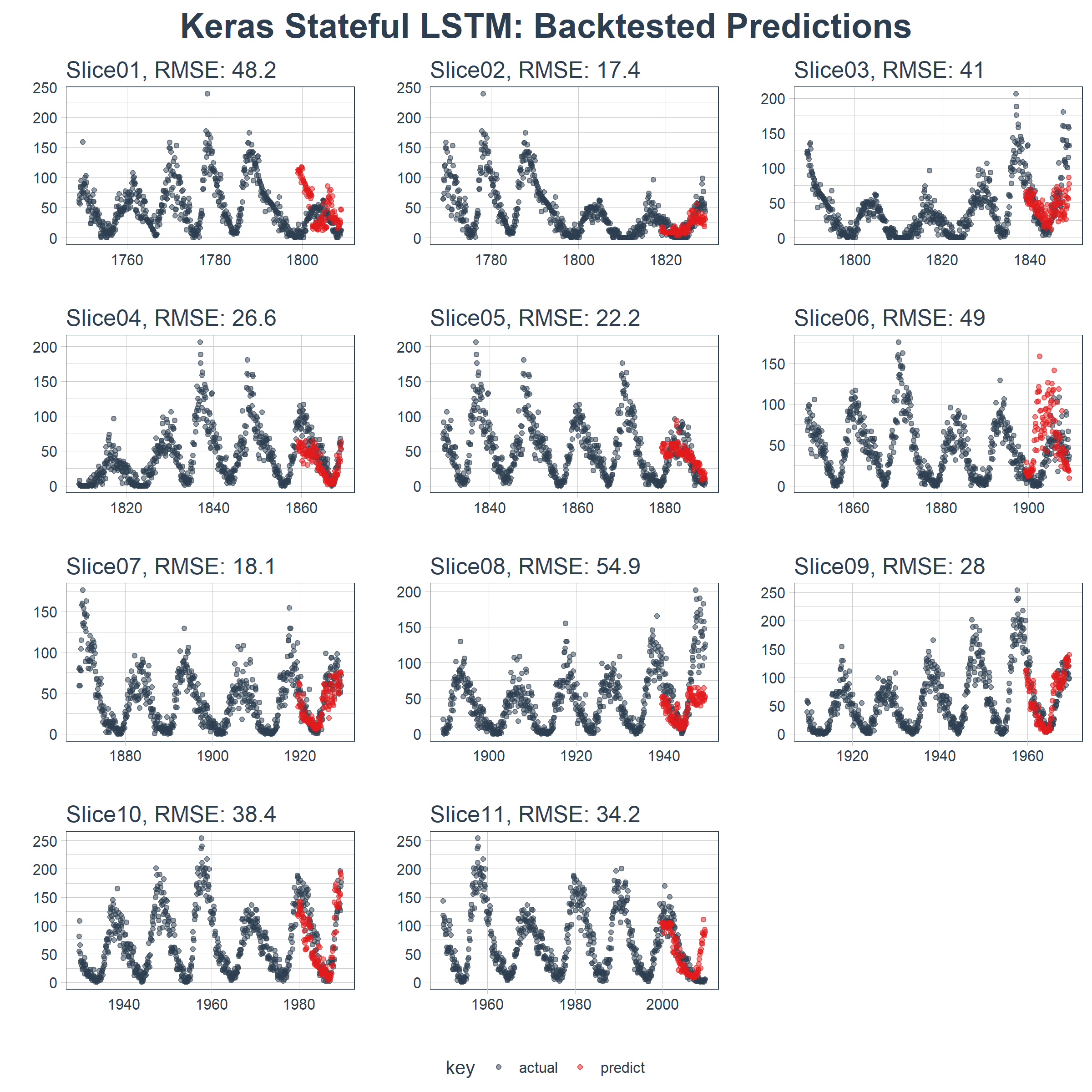
结果在这里。在一个不容易预测的数据集上,这是相当令人印象深刻的!
sample_predictions_lstm_tbl %>%
plot_predictions(
predictions_col = predict,
alpha = 0.5,
size = 1,
base_size = 10,
title = "Keras Stateful LSTM: Backtested Predictions")
5.3 预测未来 10 年的数据
我们可以通过调整预测函数来使用完整的数据集预测未来 10 年的数据。新函数 predict_keras_lstm_future() 用来预测未来 120 步(或 10 年)的数据。
predict_keras_lstm_future <- function(data,
epochs = 300,
...) {
lstm_prediction <- function(data,
epochs,
...) {
# 5.1.2 Data Setup (MODIFIED)
df <- data
# 5.1.3 Preprocessing
rec_obj <- recipe(value ~ ., df) %>%
step_sqrt(value) %>%
step_center(value) %>%
step_scale(value) %>%
prep()
df_processed_tbl <- bake(rec_obj, df)
center_history <- rec_obj$steps[[2]]$means["value"]
scale_history <- rec_obj$steps[[3]]$sds["value"]
# 5.1.4 LSTM Plan
lag_setting <- 120 # = nrow(df_tst)
batch_size <- 40
train_length <- 440
tsteps <- 1
epochs <- epochs
# 5.1.5 Train Setup (MODIFIED)
lag_train_tbl <- df_processed_tbl %>%
mutate(
value_lag = lag(value, n = lag_setting)) %>%
filter(!is.na(value_lag)) %>%
tail(train_length)
x_train_vec <- lag_train_tbl$value_lag
x_train_arr <- array(
data = x_train_vec, dim = c(length(x_train_vec), 1, 1))
y_train_vec <- lag_train_tbl$value
y_train_arr <- array(
data = y_train_vec, dim = c(length(y_train_vec), 1))
x_test_vec <- y_train_vec %>% tail(lag_setting)
x_test_arr <- array(
data = x_test_vec, dim = c(length(x_test_vec), 1, 1))
# 5.1.6 LSTM Model
model <- keras_model_sequential()
model %>%
layer_lstm(
units = 50,
input_shape = c(tsteps, 1),
batch_size = batch_size,
return_sequences = TRUE,
stateful = TRUE) %>%
layer_lstm(
units = 50,
return_sequences = FALSE,
stateful = TRUE) %>%
layer_dense(units = 1)
model %>%
compile(loss = 'mae', optimizer = 'adam')
# 5.1.7 Fitting LSTM
for (i in 1:epochs) {
model %>%
fit(x = x_train_arr,
y = y_train_arr,
batch_size = batch_size,
epochs = 1,
verbose = 1,
shuffle = FALSE)
model %>% reset_states()
cat("Epoch: ", i)
}
# 5.1.8 Predict and Return Tidy Data (MODIFIED)
# Make Predictions
pred_out <- model %>%
predict(x_test_arr, batch_